High Blood Cholesterol: Causes, Risks, and Treatments
Do you know the hidden dangers in your blood? High blood cholesterol is a silent threat that can harm your heart if not managed. This article will explore the causes, risks, and ways to fight high cholesterol. It aims to help you protect your heart health.
Key Takeaways
- High blood cholesterol is a significant risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and other serious health complications.
- Lifestyle factors like an unhealthy diet and lack of exercise can contribute to high cholesterol levels.
- Genetic and medical conditions can also influence your cholesterol levels.
- Regular cholesterol screenings and monitoring are essential for early detection and management.
- Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle and, in some cases, medication can effectively lower cholesterol and reduce your risk of cardiovascular events.
What is High Blood Cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a waxy substance in your blood that is vital for your body. But having too much can cause high blood cholesterol. This increases your risk of heart disease and other serious health issues.
Understanding Cholesterol and Its Role
Cholesterol comes in two main types: HDL (high-density lipoprotein), the “good” kind, and LDL (low-density lipoprotein), the “bad” kind. HDL helps remove excess cholesterol. LDL, on the other hand, can build up in arteries, causing plaque and increasing heart disease risk.
Good Cholesterol vs. Bad Cholesterol
It’s important to keep HDL and LDL cholesterol in balance for heart health. The goal is to have a total cholesterol level under 200 mg/dL. Aim for an LDL cholesterol level below 130 mg/dL and an HDL cholesterol level of 60 mg/dL or higher. Keeping triglycerides under 150 mg/dL is also key for heart health.
Imbalanced cholesterol levels can be dangerous. High LDL cholesterol and low HDL cholesterol levels raise the risk of atherosclerosis. This condition causes plaque to build up in arteries, leading to heart disease, stroke, and other heart problems.
Causes of High Blood Cholesterol
Your lifestyle and genes can both affect your blood cholesterol levels. Knowing what causes high cholesterol is key to managing it well.
Lifestyle Factors Contributing to High Cholesterol
Many lifestyle choices can lead to high cholesterol. Smoking, too much stress, and drinking too much alcohol can hurt your cholesterol levels. Eating foods high in bad fats and not moving enough can also affect your cholesterol.
- Smoking: Smoking lowers your HDL (good) cholesterol and increases your LDL (bad) cholesterol.
- Stress: Chronic stress can raise your triglyceride and LDL cholesterol levels.
- Alcohol: Drinking too much alcohol can increase your triglycerides and lower your HDL cholesterol.
- Unhealthy diet: A diet high in saturated and trans fats can raise your LDL cholesterol.
- Lack of exercise: Regular physical activity can boost your HDL cholesterol and lower your LDL cholesterol.
Genetic and Medical Conditions Affecting Cholesterol Levels
Some genes and health conditions can also raise your cholesterol. Familial hypercholesterolemia, a genetic issue, makes it hard for your body to clear LDL cholesterol. Other conditions like chronic kidney disease, diabetes, and hypothyroidism can also affect your cholesterol.
- Familial hypercholesterolemia: This genetic disorder affects the body’s ability to break down LDL cholesterol.
- Chronic kidney disease: Kidney disease can lead to a buildup of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood.
- Diabetes: Poorly managed diabetes can contribute to high triglycerides and low HDL cholesterol.
- Hypothyroidism: An underactive thyroid gland can result in elevated LDL cholesterol levels.
“High cholesterol is a silent condition that can put your heart health at risk. Understanding the causes, both lifestyle and genetic, is the first step in taking control of your cholesterol levels.”
Risk Factors for High Blood Cholesterol
Many things can make you more likely to have high blood cholesterol, also known as hyperlipidemia. Knowing these risk factors helps you take steps to keep your cholesterol healthy.
Unhealthy Diet and Lack of Exercise
Eating too much saturated and trans fats can increase your “bad” LDL cholesterol. It’s important to keep saturated fats under 10% of your daily calories. Not moving much and not exercising can also lead to unhealthy cholesterol levels.
Age, Family History, and Other Risk Factors
As you get older, your body has trouble removing LDL cholesterol from your blood. If your family has high cholesterol, you might be at higher risk because of genes. Other risks include being overweight, smoking, drinking too much alcohol, and having health issues like diabetes or kidney disease.
“High cholesterol can be a silent problem, with no obvious symptoms. But the risks it poses to your heart and overall health are very real.”
Keeping fit and eating well is key to managing your cholesterol. This helps lower your risk of heart disease and other problems linked to high blood cholesterol.
Complications of High Blood Cholesterol
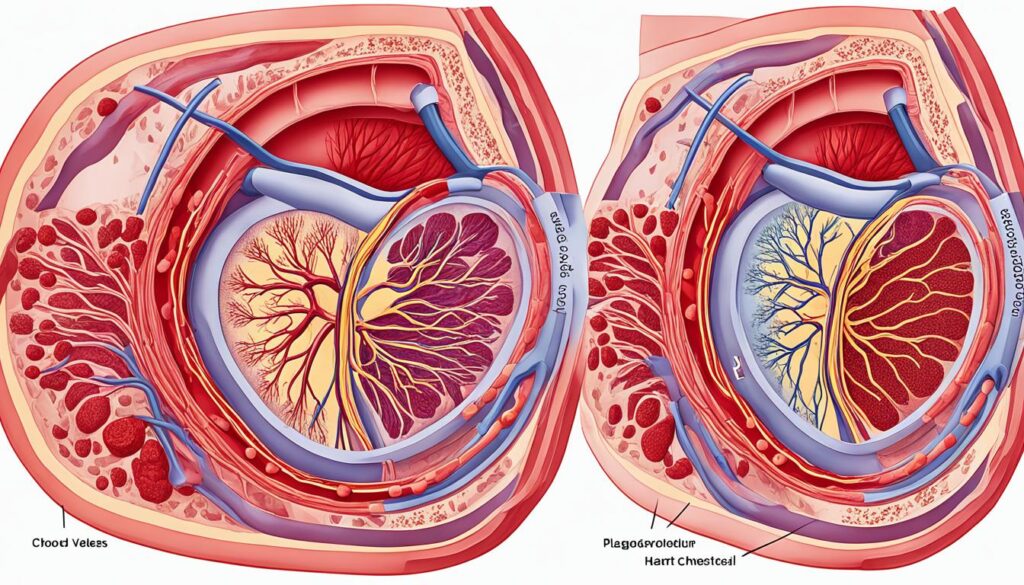
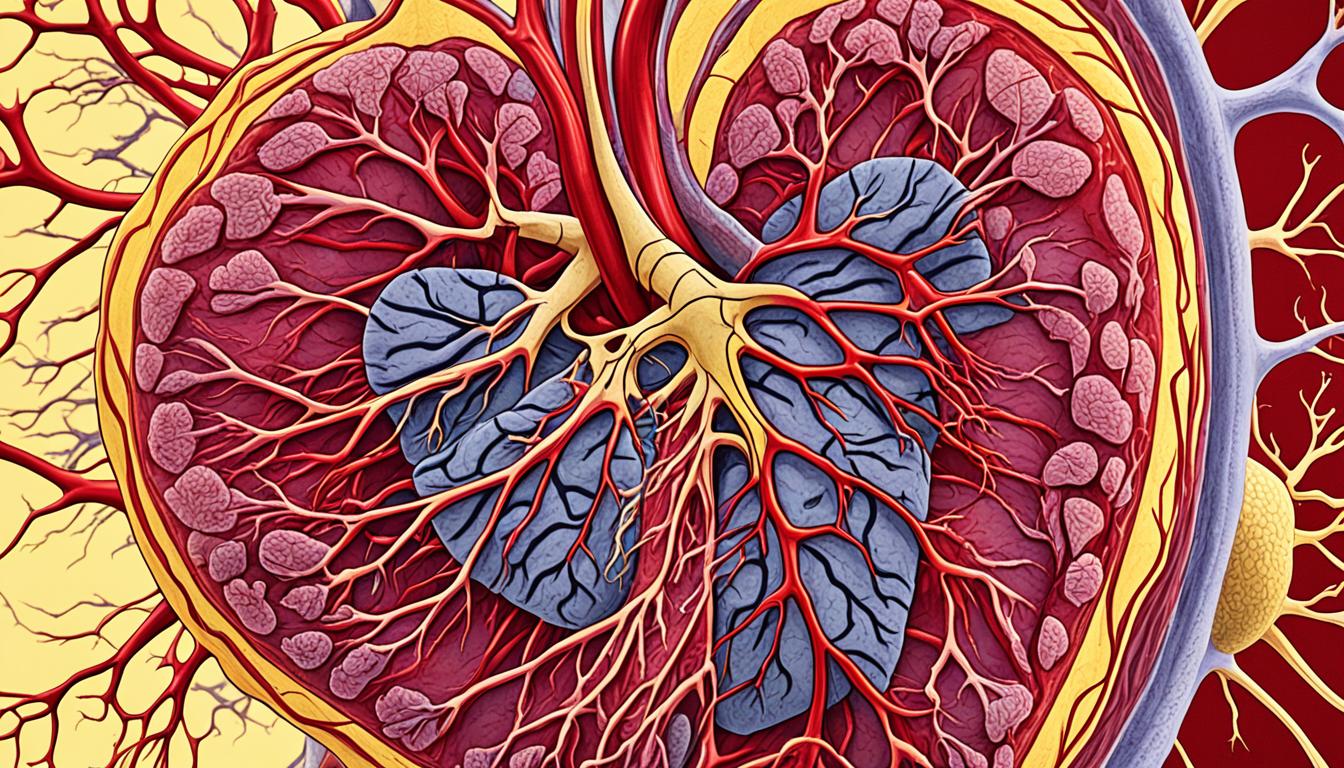
High blood cholesterol is a big health risk. It can lead to a condition called atherosclerosis. This happens when plaque, made of cholesterol, fat, and other stuff, builds up in your arteries. This reduces blood flow and raises the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other heart problems.
Atherosclerosis and Plaque Buildup
High cholesterol levels can cause plaque to gather in your arteries, a process called atherosclerosis. Over time, this plaque can make your arteries narrow and hard. This makes it harder for blood to flow. It increases your risk of heart disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease.
Heart Disease, Stroke, and Other Complications
Plaque in your arteries can really affect your heart health. If it builds up in your coronary arteries, it can block blood flow to your heart. This can cause chest pain (angina) and heart attack. Plaque in your carotid arteries raises your risk of stroke. And plaque in your peripheral arteries can cause peripheral artery disease and other issues. High blood pressure, often linked to high cholesterol, can make these risks worse.
To fight the risks of high blood cholesterol, it’s important to act early. Make healthy lifestyle changes like eating right and exercising. Your doctor may also suggest medication. Keeping an eye on your cholesterol and acting fast can prevent serious problems.
“Reducing your cholesterol levels can significantly lower your risk of heart disease, stroke, and other life-threatening conditions.”
When to Get Your Cholesterol Checked
Keeping your cholesterol levels in check is key for your health and lowering heart disease risk. The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) has guidelines on when to test your cholesterol.
Your first cholesterol check should be between ages 9 and 11. Then, test every five years after that. For adults, test every one to two years if you’re 45 to 65. If you’re over 65, test every year.
If you have a family history of high cholesterol or other risk factors, you might need more tests. These include:
- Unhealthy diet
- Lack of exercise
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Smoking
Talking to your doctor about cholesterol screening guidelines and age-based recommendations is key. This ensures you get the right level of high risk factor monitoring and care.
“Regular cholesterol checks are crucial for maintaining heart health and identifying any potential issues early on.”
By keeping an eye on your cholesterol, you can manage your heart health better. It’s never too early or late to focus on your heart’s health.
Diagnosing High Blood Cholesterol
Understanding Cholesterol Tests and Lipid Panels
Keeping your cholesterol levels healthy is key for a strong heart. Your doctor will order a blood test called a lipid panel to check for high blood cholesterol. This test looks at your total cholesterol, LDL (bad) cholesterol, HDL (good) cholesterol, and triglycerides.
Knowing your cholesterol numbers helps figure out your heart disease risk. It also guides you on how to manage your levels. Let’s explore the lipid panel and what the results mean:
- Total Cholesterol: This measures the total cholesterol in your blood. It should be less than 200 mg/dL.
- LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein) Cholesterol: Known as “bad” cholesterol, LDL can clog arteries, raising heart disease risk. Aim for a level below 100 mg/dL.
- HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) Cholesterol: HDL is your “good” cholesterol, helping remove excess cholesterol. Try to keep it above 60 mg/dL.
- Triglycerides: These are fats in your blood. High levels, linked to a bad diet and lack of exercise, also raise heart disease risk. Keep them under 150 mg/dL.
Your doctor will use your cholesterol test results to assess your heart disease risk. They’ll then create a plan to help you keep your cholesterol in check.
| Cholesterol Measurement | Optimal Range |
|---|---|
| Total Cholesterol | Less than 200 mg/dL |
| LDL Cholesterol | Less than 100 mg/dL |
| HDL Cholesterol | 60 mg/dL or higher |
| Triglycerides | Less than 150 mg/dL |
High blood cholesterol: its causes, risks, and treatment methods
High blood cholesterol is a major health issue that can cause atherosclerosis. This is when plaque builds up in arteries, raising the risk of heart disease and stroke. Knowing the causes, risks, and treatments is key to keeping your heart healthy.
Unhealthy lifestyle choices, like eating too much saturated and trans fats, not moving enough, and genetics, can cause high blood cholesterol. Some medical conditions, like diabetes and hypothyroidism, can also raise cholesterol levels.
High blood cholesterol brings big risks. Too much LDL (bad) cholesterol and not enough HDL (good) can make arteries narrow. This can lead to heart attack, stroke, and other heart problems.
But, there are ways to handle high blood cholesterol. Lifestyle changes, like eating right and moving more, can help lower cholesterol. Medications, like statins, bile acid sequestrants, and PCSK9 inhibitors, can also be used to lower cholesterol fast and well.
Checking your cholesterol regularly and working with your doctor to find the best treatment is crucial. This helps keep your heart healthy and lowers the risks of high blood cholesterol.
“Lowering LDL cholesterol leads to lower rates of cardiac events such as heart attacks, strokes, and the need for stent placement or coronary bypass surgery.”
By learning about high blood cholesterol’s causes, risks, and treatments, you can take steps to protect your heart. This can help prevent serious heart problems.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing High Cholesterol
Struggling with high cholesterol? Making lifestyle changes can help. By eating right and moving more, you can control your cholesterol. This can lower your risk of heart disease.
Adopting a Heart-Healthy Diet
Eating less saturated and trans fats and more fruits, veggies, and whole grains can help. Whey protein in dairy products can also lower bad cholesterol and blood pressure.
Include more heart-healthy foods in your diet, such as:
- Whole grains
- Fruits and vegetables
- Lean proteins like fish and poultry
- Nuts and legumes
- Healthy oils like olive or avocado oil
These changes can help you manage your high cholesterol.
Increasing Physical Activity and Exercise
Regular exercise is key for managing high cholesterol. Activities like brisk walking, swimming, or cycling for 30 minutes five times a week can boost your good cholesterol. This improves heart health and lowers heart disease risk.
Small changes like taking the stairs or daily walks also help. Find fun activities to make them part of your life.
By making these lifestyle changes, you can actively manage your high cholesterol. Remember, it may take 6 to 12 months to see results. Stay patient and keep up your efforts.
Medications for Treating High Cholesterol
Along with lifestyle changes like eating well and exercising, you might need medications to control high cholesterol. Statins are the most common type of cholesterol-lowering drug.
Statins and Other Cholesterol-Lowering Drugs
Statins lower LDL (bad) cholesterol by reducing its production in the liver. They are often the first choice for high cholesterol. Other drugs, like bile acid sequestrants and fibrates, can also help lower cholesterol, sometimes with statins.
Statins can greatly reduce LDL and triglycerides and slightly raise HDL (good) cholesterol. But, they might cause muscle pain, raise blood sugar, and lead to stomach issues.
Cholesterol absorption inhibitors, such as Ezetimibe, can lower LDL and slightly affect triglycerides and HDL. Side effects might include stomach pain and muscle soreness.
PCSK9 inhibitors, like Alirocumab and Evolocumab, are for very high LDL levels or statin intolerance. They can cause itching and swelling at the injection site.
Bile acid sequestrants, including Cholestyramine, can reduce LDL but may cause constipation and stomach issues.
Combination medications mix different cholesterol-lowering drugs for better results. They can increase HDL and lower LDL and triglycerides. But, they might also raise the risk of side effects like stomach pain and muscle soreness.
Fibrates, such as Fenofibrate, can lower triglycerides and slightly reduce LDL while raising HDL. Side effects might include nausea and muscle pain.
Other options like Niacin and Omega-3 fatty acids can also help with high cholesterol. They work differently and may have other side effects.
Always talk to your healthcare provider to find the best cholesterol medication for you, considering your health history.
Preventing High Blood Cholesterol
Starting a healthy lifestyle early is crucial for avoiding high blood cholesterol and its risks. By making smart choices, you can manage your cholesterol levels. This reduces the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other serious conditions.
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle from an Early Age
Creating healthy habits early is the key to preventing high cholesterol. This means:
- Eating foods low in saturated and trans fats helps. Choose lean meats, seafood, and whole grains, and eat more fruits and vegetables.
- Regular exercise is important, like 30-60 minutes of moderate activity most days. It keeps you at a healthy weight and lowers cholesterol.
- Stay away from smoking and limit alcohol to protect your heart health.
By sticking to these habits from a young age, you can greatly lower your risk of high cholesterol and its health problems.
“Eating lots of foods high in saturated fat and trans fat may contribute to high cholesterol and related conditions, such as heart disease.”
| Healthy Habits | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Eating a heart-healthy diet | Lowers bad (LDL) cholesterol and increases good (HDL) cholesterol |
| Engaging in regular physical activity | Helps maintain a healthy weight and lower cholesterol levels |
| Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol | Reduces the risk of heart disease and other cholesterol-related conditions |
Choosing a healthy lifestyle early helps you avoid high blood cholesterol. It also protects your heart health for the long run.
High Cholesterol in Children and Adolescents
High cholesterol isn’t just a worry for grown-ups; it can hit kids and teens too. The American Heart Association says 1 in 5 teens deal with high cholesterol. Catching and managing cholesterol in children early is key to avoiding heart disease later.
Kids and teens with high pediatric cholesterol might not show any signs. So, regular early screening is a must. Kids should get their first cholesterol check between 9 to 11 years old, then every 5 years after that. Those with a family history of heart issues might need tests sooner.
Many things can lead to high cholesterol in kids, like eating badly, not moving enough, being overweight, or certain genetic conditions. Keeping an eye on high cholesterol in children is vital for their heart health as they grow.
| Cholesterol Type | Acceptable Levels | Borderline Levels | Abnormal Levels |
|---|---|---|---|
| LDL (bad cholesterol) | 110-129 mg/dl | ≥130 mg/dl | |
| HDL (good cholesterol) | >45 mg/dl | 40-45 mg/dl | |
| Total Cholesterol | 170-199 mg/dl | ≥200 mg/dl | |
| Triglycerides (0-9 years) | 75-99 mg/dl | ≥100 mg/dl | |
| Triglycerides (10-19 years) | 90-129 mg/dl | ≥130 mg/dl |
For high cholesterol in children, the first step is changing their lifestyle. This means eating right and staying active. If a child over 10 keeps having high cholesterol, doctors might suggest medicine. Catching high cholesterol early helps kids and teens keep their hearts healthy for the future.
Managing High Cholesterol with Other Conditions
Some health issues can change how high cholesterol affects you. If you have high cholesterol, knowing how it interacts with other health problems is key. This helps you manage it better.
High Cholesterol and Diabetes
Diabetes raises the risk of high cholesterol, which can lead to heart disease. For people with diabetes, keeping cholesterol levels healthy is crucial. High blood sugar and high LDL (bad) cholesterol can cause serious heart problems.
High Cholesterol and Kidney Disease
Kidney disease can change cholesterol levels, making triglycerides higher and HDL (good) cholesterol lower. This increases heart disease risk for those with kidney issues. Managing high cholesterol with kidney disease needs a detailed plan. Healthcare providers must work together closely.
Dealing with high cholesterol and other health issues requires a full plan. This plan should include lifestyle changes, managing medications, and regular check-ups. It helps keep cholesterol levels healthy and lowers the risk of more problems.
The Importance of Regular Monitoring
It’s key to watch your cholesterol levels closely to manage high blood cholesterol and lower your risk of health problems. Your doctor will tell you how often to get your cholesterol checked. This depends on your age, health, and risk factors.
By regularly monitoring your cholesterol, you and your doctor can keep an eye on changes. This helps you make smart choices about treatments and lifestyle changes to keep your cholesterol healthy.
- The National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI) suggests cholesterol screenings every 1 to 2 years for men ages 45 to 65 and for women ages 55 to 65.
- People over 65 should get cholesterol tests annually.
- A cholesterol test usually requires fasting for 9 to 12 hours before the test, though some tests don’t need fasting.
By tracking your cholesterol numbers and any changes, you can work with your healthcare provider. Together, you can spot issues early and manage your cholesterol levels. This lowers your risk of heart disease, stroke, and other serious health problems.
“Regularly monitoring your cholesterol levels is the key to maintaining a healthy heart and preventing serious cardiovascular problems down the road.”
Conclusion
High blood cholesterol is a serious health issue that needs your focus and action. Knowing the causes, risks, and ways to treat it helps you protect your heart health. This can lower your chance of heart disease and stroke.
By making lifestyle changes, checking your levels often, and possibly taking medicine, you can handle your high cholesterol. This can also cut down your risk of these serious health problems.
From this article, it’s clear that keeping your cholesterol in check is key for your health. High cholesterol might not show symptoms, but catching it early and treating it can change your health for the better. Eating right, exercising regularly, and other lifestyle changes can help you manage your cholesterol and lower your risk of heart issues.
Handling high blood cholesterol is up to you and requires ongoing care. Work with your doctor to make a plan that suits you. With the right steps, you can lessen the effects of high cholesterol and live a healthier life.